Azithromycin Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Azithromycin pelvic inflammatory disease. Bowden FJ Jacups S Huffman S Savage J OBrien M. Do not prescribe azithromycin to. A prospective randomized controlled trial.
Azithromycin is active against Mycoplasma genitalum considered an STDAn exception is M. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent long term sequelae. All the three treatment combinations were found to be equally effective in the syndromic management of pelvic inflammatory disease.
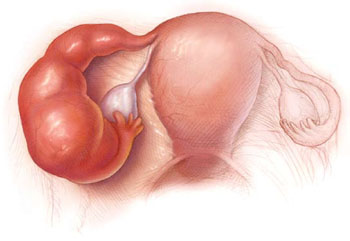
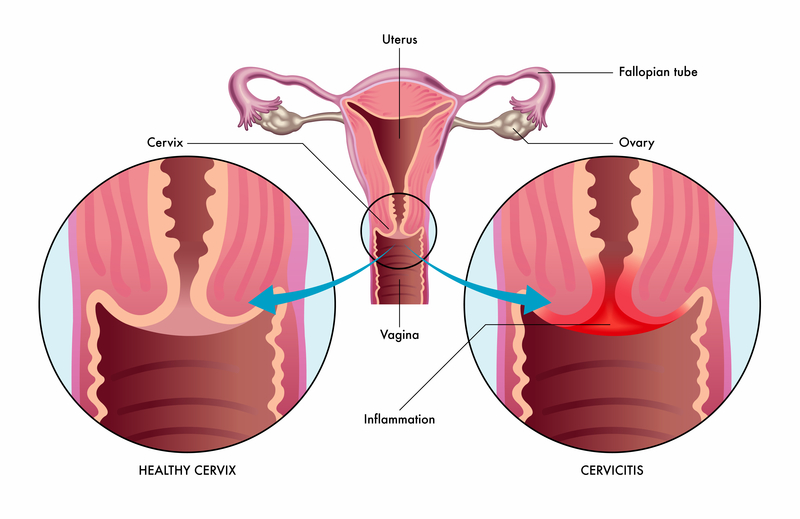
Not in a single dose. To conduct such a trial we followed the CONSORT recommendations. Overview A syndrome comprising a spectrum of inflammatory disorders of the upper female genital tract including any combination of endometritis salpingitis tubo-ovarian abscess and pelvic peritonitis.
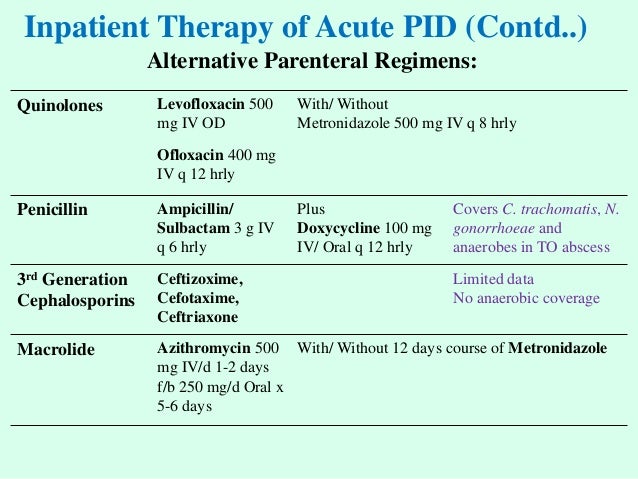
To evaluate the equivalence of ceftriaxone plus doxycycline or azithromycin for cases of mild pelvic inflammatory disease PID. Pelvic inflammatory disease is an infection of the upper female genital tract caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae Chlamydia trachomatis or both although it may also be caused by microorganisms that. 500 mg orally once a day for 3 days OR 500 mg orally as a single dose on day 1 followed by 250 mg orally once a day on days 2 to 5.
Ciprofloxacin-tinidazole combination fluconazole- azithromicin-secnidazole-kit and doxycycline- metronidazole combination therapy in syndromic management of pelvic inflammatory disease. 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines Pelvic Inflammatory Disease PID June 4 2015 Resources for Clinicians. It is continuously updated and integrates the most recent STD Treatment Guidelines.
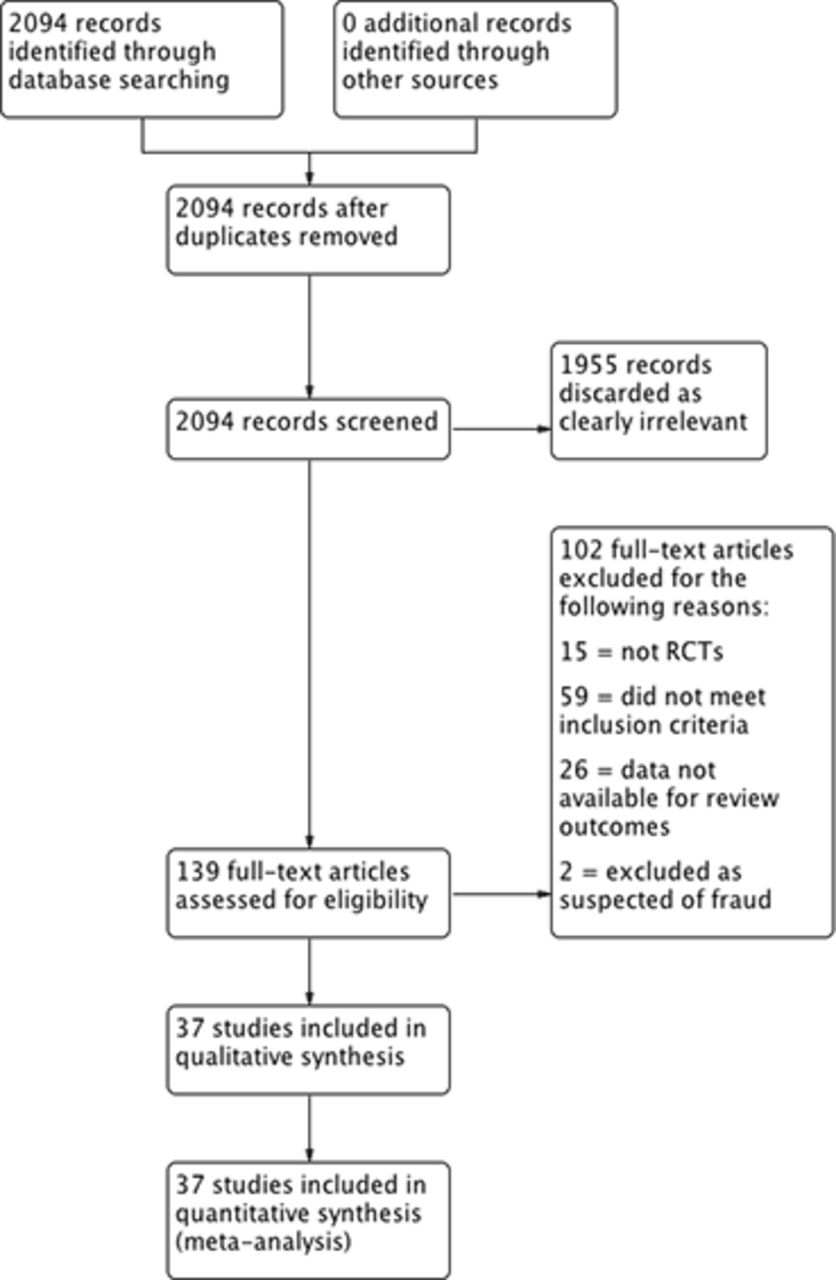
Between 1992 and 2006 5 randomized clinical trials of moxifloxacin 1 trial ofloxacin 1 trial clindamycin-ciprofloxacin 1 trial and azithromycin 2 trials treatment among women with mild to. Development of azithromycin intravenous formulation would bring the clinical benefit to patients with pelvic inflammatory disease PID in Japan. Efficacy and safety of azithromycin as monotherapy or combined with metronidazole compared with two standard multidrug regimens for the treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease.
Pregnant women due to the limited data available on the use of azithromycin in pregnant women the manufacturer advises that it should be avoided unless a. Treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease PID should provide high rates of clinical and microbiological cure for a range of pathogens and should ultimately prevent reproductive morbidity.
Bowden FJ Jacups S Huffman S Savage J OBrien M.
Between 1992 and 2006 5 randomized clinical trials of moxifloxacin 1 trial ofloxacin 1 trial clindamycin-ciprofloxacin 1 trial and azithromycin 2 trials treatment among women with mild to. Ciprofloxacin-tinidazole combination fluconazole- azithromicin-secnidazole-kit and doxycycline- metronidazole combination therapy in syndromic management of pelvic inflammatory disease. To evaluate the equivalence of ceftriaxone plus doxycycline or azithromycin for cases of mild pelvic inflammatory disease PID. Hominis which is not susceptible to macrolides. Azithromycin Prescribing information Pelvic inflammatory disease CKS. Doxycycline and fluoroquinolones eg. Bowden FJ Jacups S Huffman S Savage J OBrien M. 500 mg orally once a day for 3 days OR 500 mg orally as a single dose on day 1 followed by 250 mg orally once a day on days 2 to 5. Clinical presentation varies widely in both severity and symptomatology.
To evaluate the equivalence of ceftriaxone plus doxycycline or azithromycin for cases of mild pelvic inflammatory disease PID. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent long term sequelae. Our initial hypothesis was that azithromycin and doxycycline were equivalent drugs for treating mild pelvic inflammatory disease. Azithromycin is active against Mycoplasma genitalum considered an STDAn exception is M. Clinical presentation varies widely in both severity and symptomatology. Azithromycin and pelvic inflammatory disease in the Northern Territory. Overview A syndrome comprising a spectrum of inflammatory disorders of the upper female genital tract including any combination of endometritis salpingitis tubo-ovarian abscess and pelvic peritonitis.




















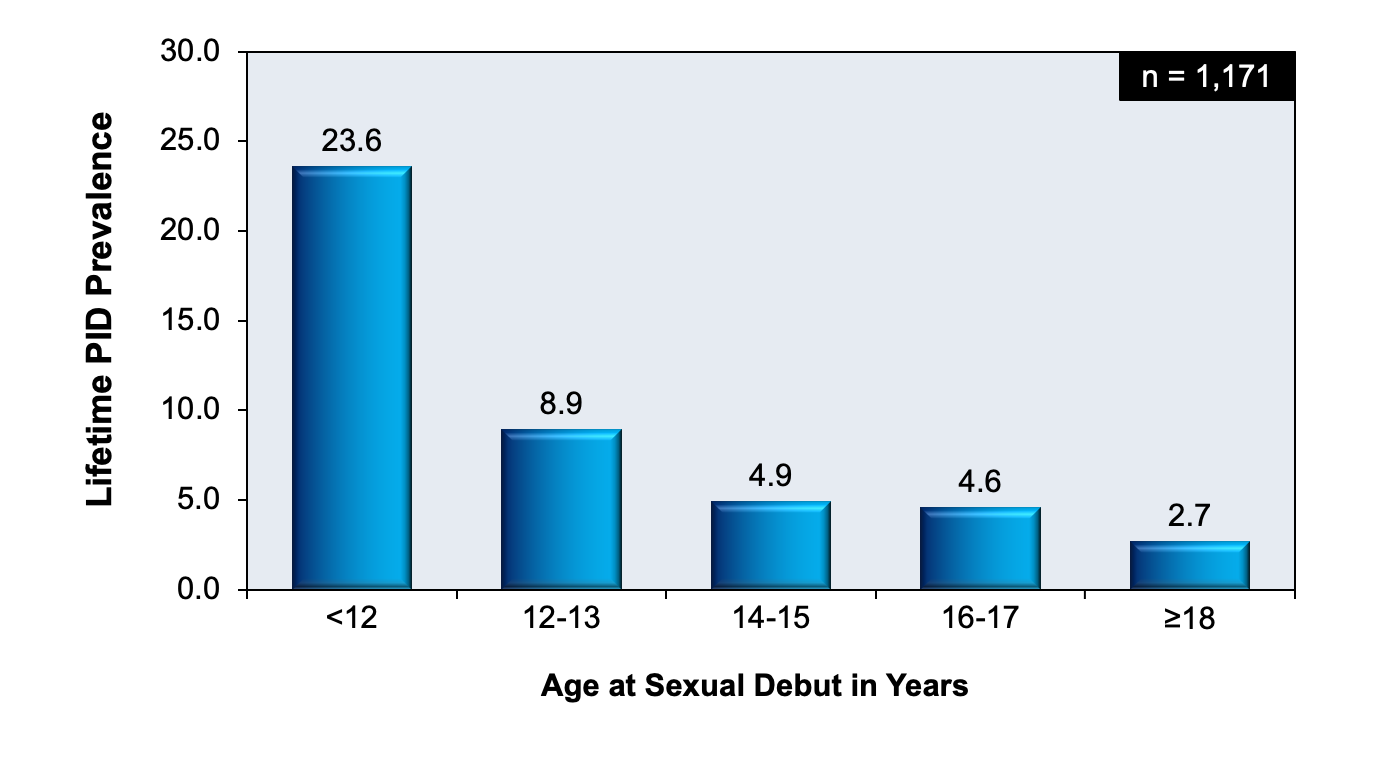

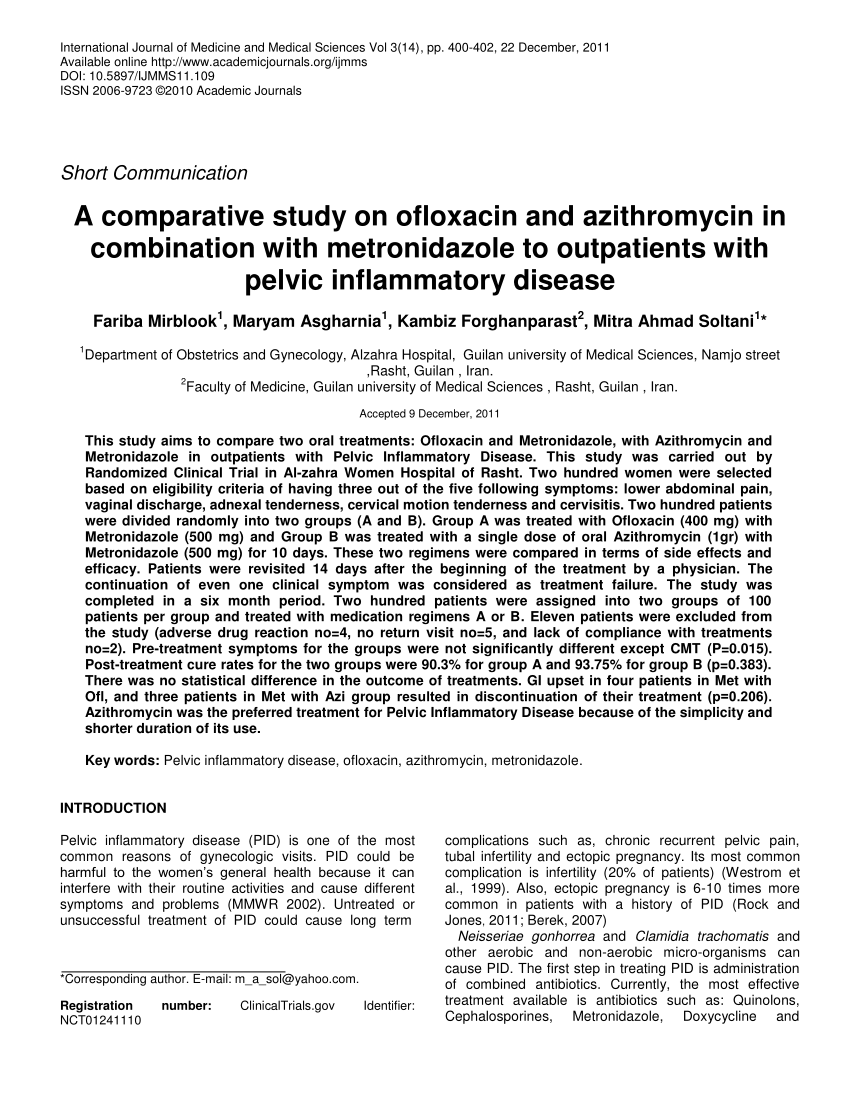

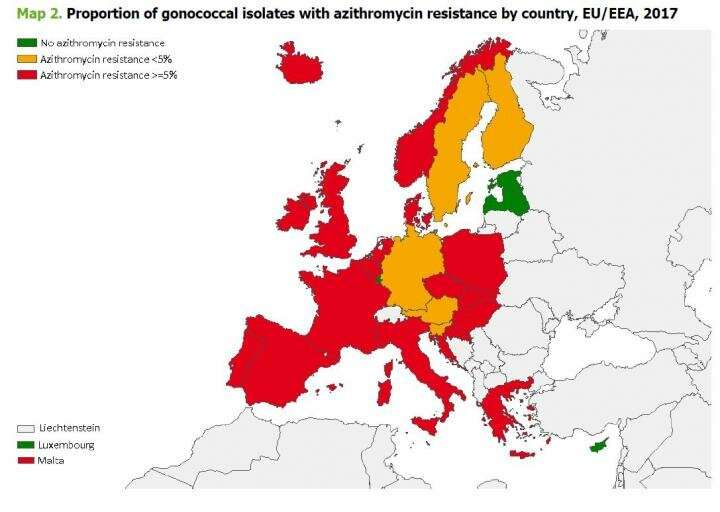

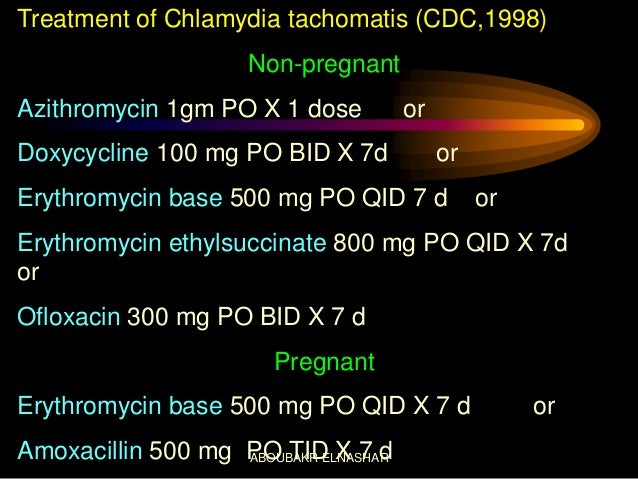





Post a Comment for "Azithromycin Pelvic Inflammatory Disease"