Neurocognitive Disorder Due To Alzheimer's Disease
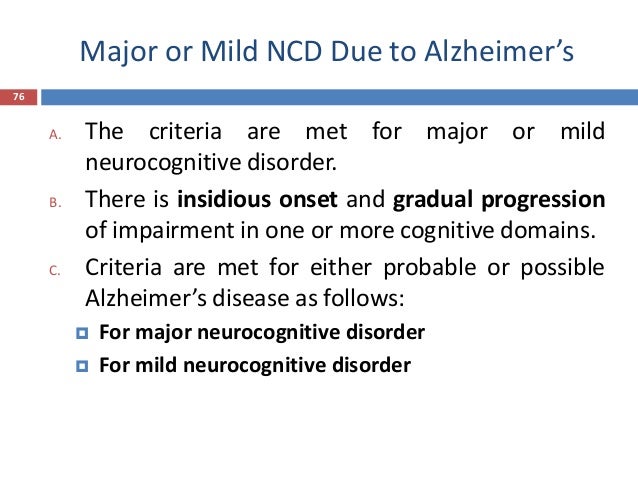
Neurocognitive disorder due to alzheimer's disease. A three-step evaluation process. Major or Mild NCD due to Alzheimers disease AD Insidious onset gradual progression Major NCD. Step one determining a neurocognitive disorder.
Mild neurocognitive disorder co-occurrent and due to human immunodeficiency virus infection. Alzheimers disease is the most prevalent neurodegerative disorder. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
The American Psychiatric Associations DSM-5 of 2013 suggests in its diagnostic criteria and text explicitly or implicitly a diagnostic approach for Neurocognitive Disorders that includes. The anticipated effect of novel. They are typically prescribed for Alzheimers disease but may also be used to manage other neurocognitive disorders.
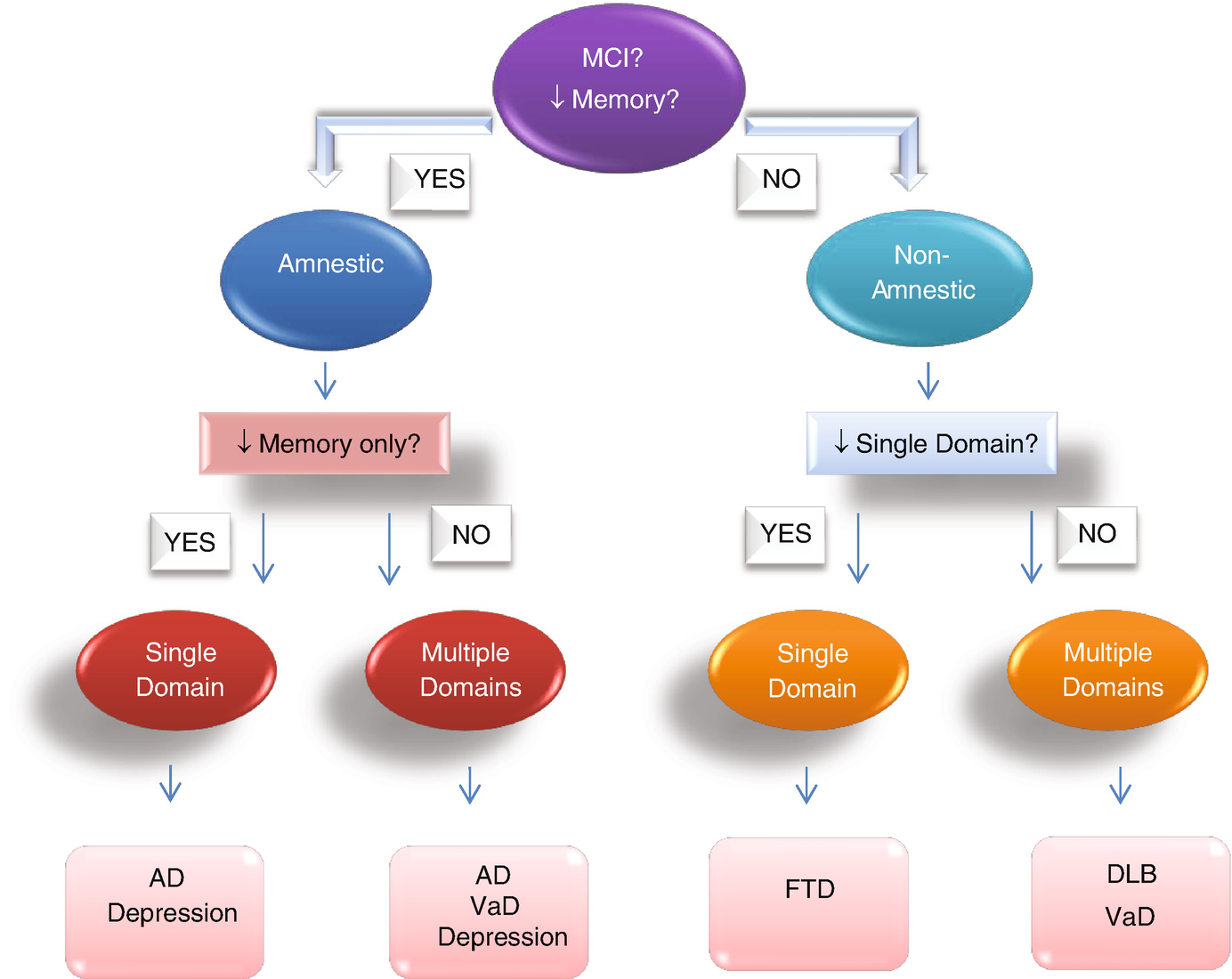
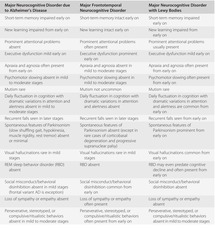
2 or more cognitive domains impaired unlike other Major NCDs impaired IADLs Mild NCD. Alzheimer disease is a primary degenerative cerebral disease of unknown etiology with characteristic neuropathological and neurochemical features. Mild neurocognitive disorder co-occurrent and due to lewy body disease.
Major neurocognitive disorder known previously as dementia is a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with independence and daily life. Mild neurocognitive disorder co-occurrent and due to frontotemporal lobar degeneration. This can be done in one of two ways.
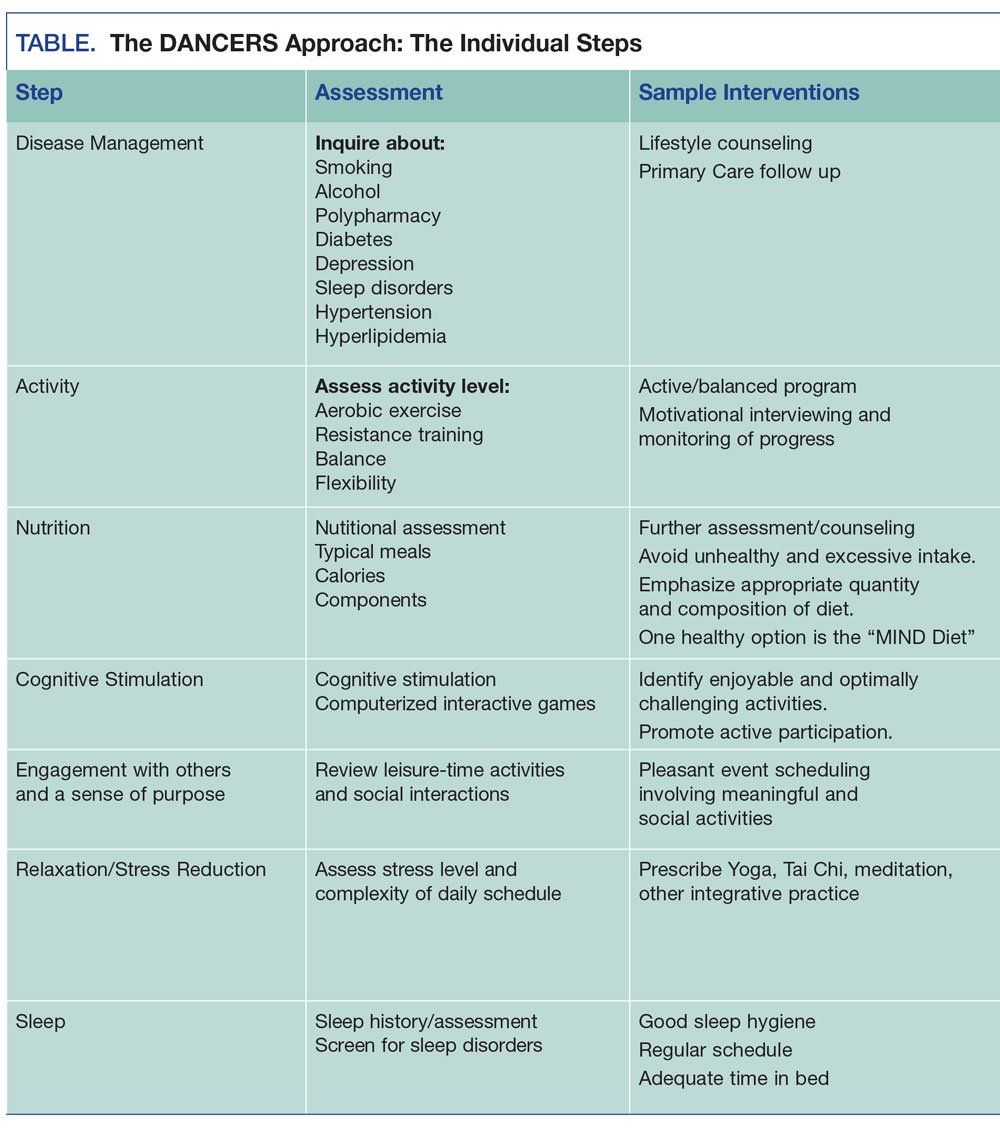
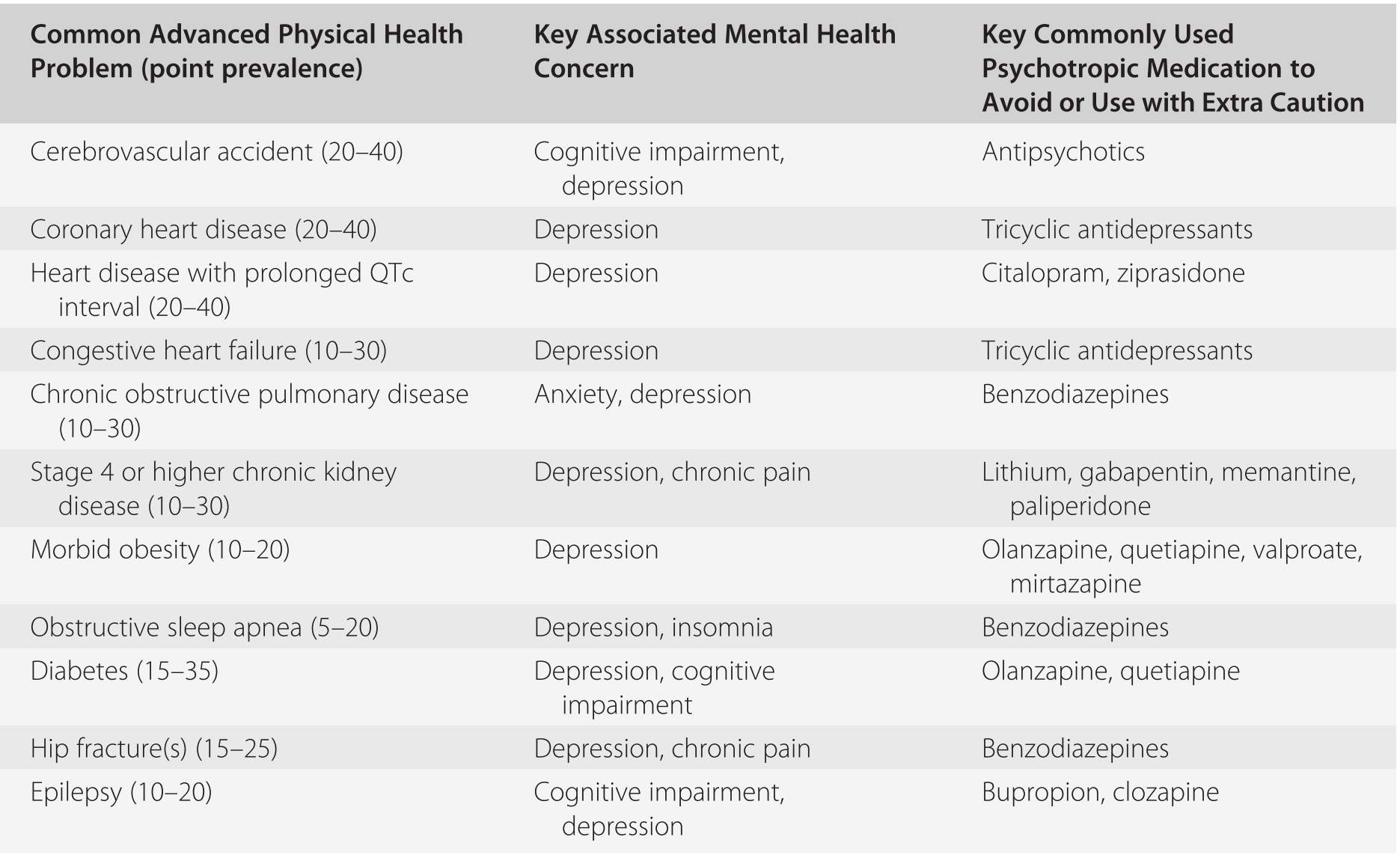
In addition to cognitive symptoms psychiatric complications are common and are major contributors to impairments in quality of life for the individual and families and significantly impact health care costs. 1 or more cognitive domains impaired IADLs intact. Alzheimers disease AD and other neurocognitive disorders are one of the major classes of disorders relevant to older adults.
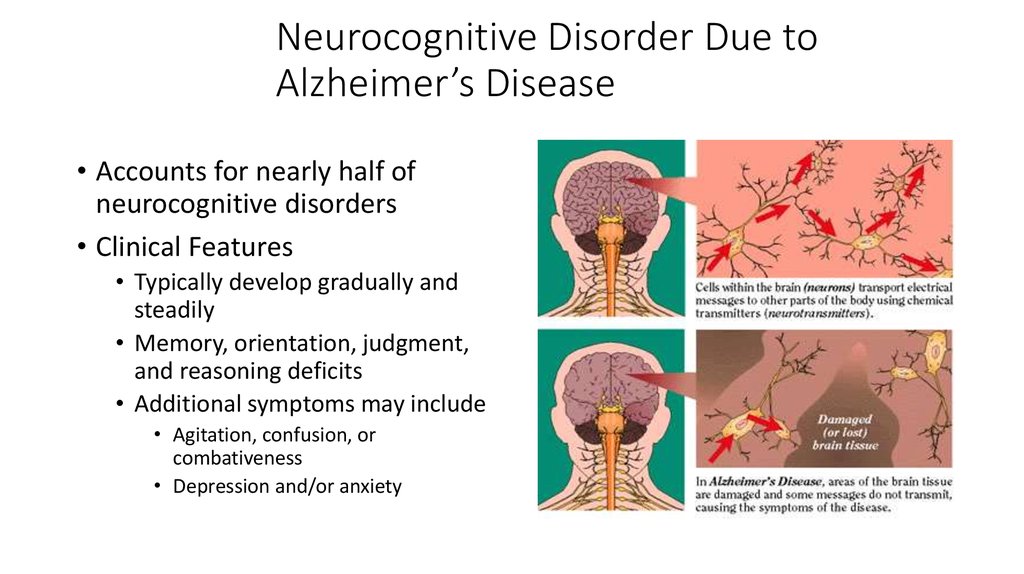
Neurocognitive Disorder due to Alzheimers Disease. Alzheimers disease AD is a slowly progressive neurocognitive disorder with a preclinical phase in which the individual may be asymptomatic for many years.
They are typically prescribed for Alzheimers disease but may also be used to manage other neurocognitive disorders.
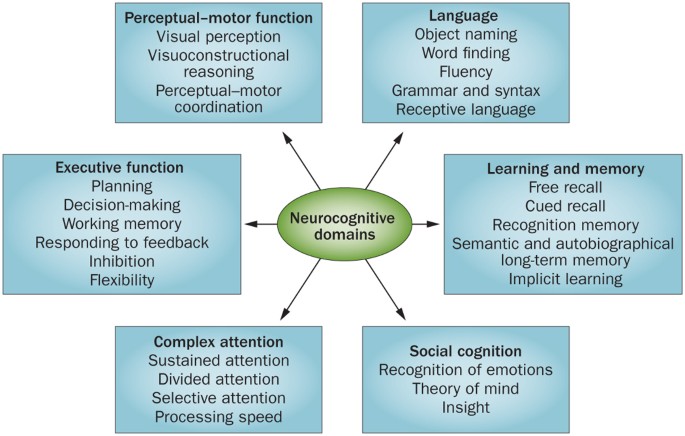
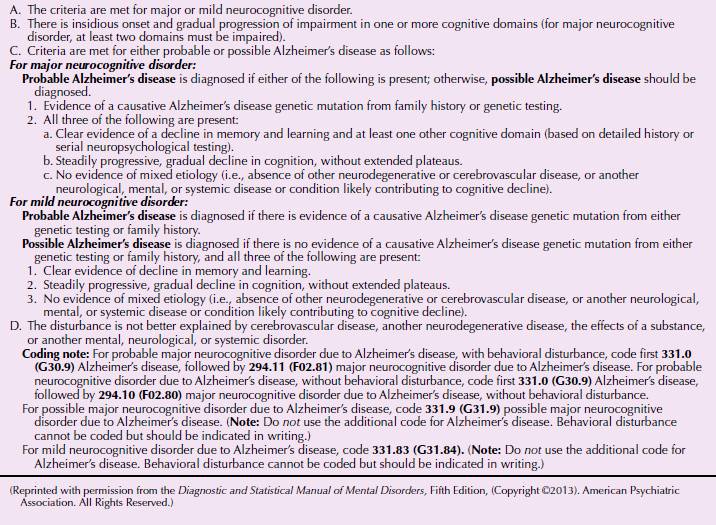
In addition to cognitive symptoms psychiatric complications are common and are major contributors to impairments in quality of life for the individual and families and significantly impact health care costs. The anticipated effect of novel. This preclinical phase is followed by a period generally termed mild cognitive impairment MCI of impaired cognition and possible neuropsychiatric symptoms without functional deficit. Current therapies enhance cognition without changing the rate of decline in AD 3. 2 or more cognitive domains impaired unlike other Major NCDs impaired IADLs Mild NCD. An auxiliary table containing six defined cognitive domains and twenty two subdomains examples of symptoms or observations and assessments b. Alzheimers disease is the most prevalent neurodegerative disorder. Major neurocognitive disorder known previously as dementia is a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with independence and daily life. 1 or more cognitive domains impaired IADLs intact.
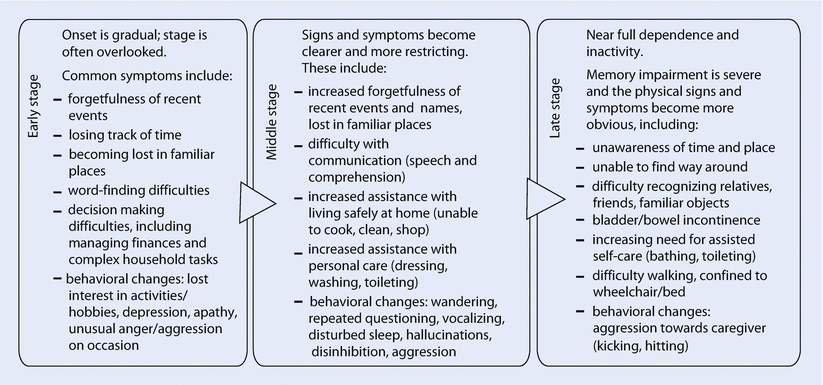
Furthermore what is major neurocognitive disorder. Alzheimers disease AD is a slowly progressive neurocognitive disorder with a preclinical phase in which the individual may be asymptomatic for many years. The different areas of the brain affected. Major neurocognitive disorder known previously as dementia is a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with independence and daily life. The disorder is usually insidious in onset and develops slowly but steadily over a period of several years. Alzheimers disease is marked by more rapid cognitive decline often starting earlier in life 2. While the primary symptom of Alzheimers disease is the gradual progression of impairment in cognition it is important to also identify concrete evidence of cognitive decline.


































Post a Comment for "Neurocognitive Disorder Due To Alzheimer's Disease"